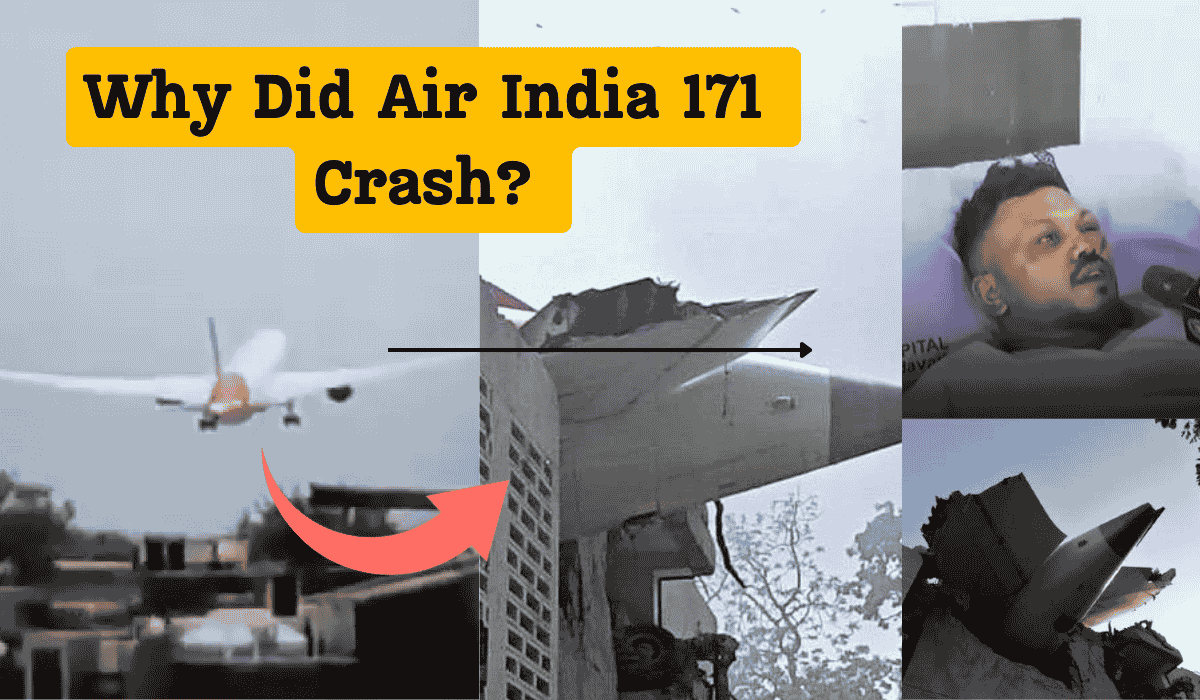
On June 12th, an Air India flight, AI 171, traveling from Ahmedabad to London, ended in tragedy, leaving many people in shock. The plane, a Boeing 787 Dreamliner, which is typically known for its safety, crashed shortly after takeoff. This unexpected disaster of the Air India 171 crash has raised numerous questions for investigators.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what may have caused this tragic event, discuss various possibilities, and highlight the challenges involved in ensuring air travel safety.
Table of Contents
The Start of the Incident
The flight had arrived in Ahmedabad from Delhi, underwent refueling, and boarded passengers as usual. The takeoff appeared normal, but shortly after reaching an altitude of around 400 feet, the aircraft began to descend. The unexpected, sudden descent of the aircraft was shocking, and it was difficult to understand how a perfectly functional aircraft could suddenly crash to the ground.
Unusual Observations from the Air India 171 crash
Initial analysis of the crash footage reveals three unusual aspects of the plane’s configuration during takeoff:
- Retracted Wings: The plane’s wings were in a retracted position, meaning the slats and flaps were not extended.
- Landing Gear Extended: The landing gear remained deployed rather than retracting as is standard during takeoff.
- Nose Upward: The plane’s nose was angled upward, as if it were attempting to take off.
This combination of factors presents a contradictory configuration, indicating that the plane was attempting to take off while simultaneously trying to land.
Before moving ahead, let’s understand the routine takeoff procedures
Typically, during takeoff, several key actions occur:
- Wing Extension: The wings’ slats and flaps extend, creating an angle of attack (typically 10-15 degrees) that allows the wings to generate lift.
- Nose Elevation: The plane’s nose rises, further contributing to lift.
- Landing Gear Retraction: The wheels retract into the plane to reduce drag.
These actions create an aerodynamic structure that enables the plane to lift off the ground successfully. Once the plane reaches a safe altitude, the wing extensions are retracted to optimize for cruising speed.
The aftermath
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner crash left people around the world in a state of shock. Families rushed to the civil hospital in Ahmedabad, India, hoping to hear news about their loved ones. Sadly, only one person survived out of the 242 passengers on the flight. The pilots had very little time to respond to the emergency—just over half a minute—and only seconds to react before the plane started its dangerous fall.
Searching for Answers
The official investigation of the Air India 171 crash is underway. It’s important to note that these are educated assumptions and should not be considered definitive findings.
Unanswered Questions
Several questions remain unanswered, fueling speculation and concern:
- Why did the aircraft become airborne so late?
- If an engine failed, why was there no visible smoke or fire?
- How could both engines fail simultaneously, a scenario considered statistically improbable by aircraft manufacturers?
- Was the aircraft’s loading correct?
- Why weren’t the landing gears retracted?
- Was the Ram Air Turbine (RAT) deployed?
- Did the aircraft take off from an intersection or the full length of the runway?
- Did the aircraft take off at 9979 feet instead of 9200 feet?
Exploring Potential Causes: A Deep Dive
Let’s examine some of the potential causes that have been considered:
1. Flap Retraction
The theory that flap retraction caused the crash has been largely dismissed. Evidence from the engine parts found at the crash site suggests that the engines were not operating at full power when the aircraft struck the ground, which makes it unlikely that problems with the flaps caused the accident.
2. Dual Engine Failure: The Primary Suspect
The most plausible explanation was a dual-engine failure. Modern aircraft are designed to fly on a single engine, even when fully loaded. Therefore, a simultaneous failure of both engines would be catastrophic.
3. Bird Strike: Unlikely
While bird strikes are a common concern, the circumstances surrounding the crash make this scenario unlikely. The weather in Ahmedabad, India, at the time was clear and hot, conditions not typically associated with bird activity. Furthermore, there were no visible signs of bird strikes in the available footage of the crash. Aircraft engines are also certified to withstand the impact of a certain number of birds.
4. Foreign Object Damage (FOD)
Foreign Object Damage, which occurs when debris on the runway is sucked into the engine and causes harm, is unlikely in this case. There were no signs of fire, smoke, or loud noises, which are usually associated with this kind of problem.
5. Weather or Wind Shear
Modern weather radar systems are pretty sophisticated and can identify dangerous wind conditions, known as wind shear. Pilots receive training to postpone or cancel takeoffs when they sense these risks. During the time of the crash, the weather was clear, which makes it unlikely that wind shear played a role in the accident.
6. One Engine Failed on Ground, One After Takeoff: A Possible Scenario
This scenario suggests that one engine failed on the ground, leading to a delayed takeoff, and the second engine failed shortly after becoming airborne. This could explain why the aircraft took longer to lift off.
7. Fuel Contamination: A Wild Card
Fuel contamination is unlikely, but if it were to occur, it would indicate that someone had intentionally caused it. Fuel delivery trucks are carefully inspected multiple times to ensure they are not using contaminated or substandard fuel.
Similar examples from the past Crashes
To gain further insight, it’s helpful to examine similar past incidents. Two notable examples include:
- 2008 Madrid Crash: A McDonald Douglas MD82 crashed shortly after takeoff because the wings’ slats and flaps were not extended. The investigation revealed a combination of pilot error (skipping a checklist item) and a technical issue (a deactivated alarm system that should have alerted the pilots to the error).
- 1987 Detroit Crash: A McDonald Douglas DC-9-82 crashed after failing to achieve sufficient lift and speed due to retracted wings. This crash was also attributed to human error and a failure of the alarm system.
The Importance of Independent Investigation
The investigation into the Air India 171 crash must be conducted thoroughly and independently. The Accident Investigation Board of India (AAIB) should be free from any political or administrative pressure to ensure that the actual cause of the crash is determined.
Concerns About Air India’s Safety Record
Air India has faced multiple serious allegations of safety lapses in the past, including fines, audits, suspensions, and show-cause notices. This raises important questions about how seriously Air India takes safety and whether there might be bigger issues that need to be addressed.
Prioritizing Safety
The Air India 171 crash serves as a stark reminder of the importance of prioritizing safety in aviation. Airlines, manufacturers, and regulatory agencies must collaborate to prevent such accidents in the future. This includes:
- Thorough investigations: Conducting independent and transparent investigations into all accidents and incidents.
- Addressing systemic issues: Identifying and addressing any systemic problems that may contribute to safety lapses.
- Prioritizing pilot training: Ensuring that pilots receive adequate training to handle emergencies effectively.
- Maintaining aircraft: Properly maintaining aircraft and addressing any maintenance issues promptly.
- Promoting a safety culture: Fostering a culture of safety within airlines, where employees are encouraged to report concerns without fear of reprisal.
We must await the official investigation and the release of the flight recorders to gain a complete understanding of what transpired.
Read our latest post – US Moves B-2 Stealth Bombers as Iran-Israel tensions rise